 ytt
2021-05-27
ytt
2021-05-27
 阅读:
阅读:
既然讲到了建筑,那就让我们从建筑本身入手,看看除了已经十分熟悉的building、house这些笼统的概念之外,具体不同类型的建筑分别叫什么名字:
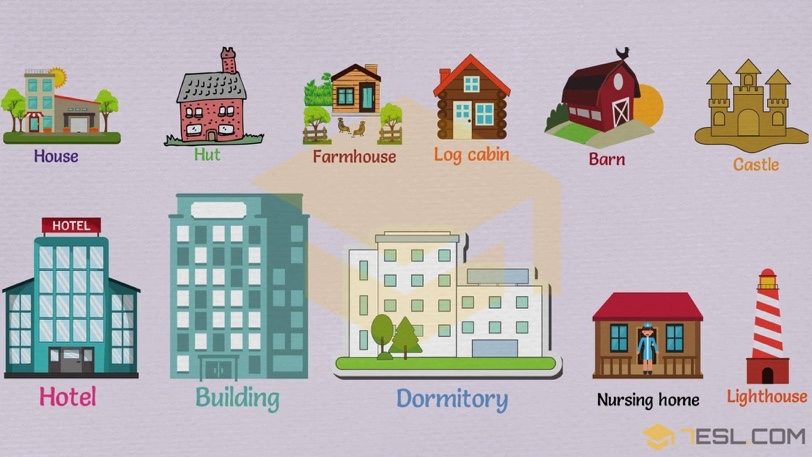
House n住宅
Hut /hʌt/ 简陋的小屋子(棚、舍)
Farmhouse /ˈfɑ:rmhaʊs/ n农场住宅,农舍
Log cabin n小木屋
(TPO54 passage1 Traditionally, cutting took place in the winter, when snow and ice made it easier to drag logs on sleds or sleighs to the banks of streams.)
Castle n城堡
Hotel n旅馆,旅社,客栈
Building n公寓大楼
Dormitory /ˈdɔ:rmətɔ:ri/ n集体宿舍
(TPO250 conversation1 Yeah, I um......I'm taking summer classes right now and they put me in Robert's Dormitory, over by the library.)
Nursing home 私人疗养院
Lighthouse 灯塔
Corridor n走廊
(TPO9 passage1 It was the midcontinental corridor between two massive ice sheets-the Laurentide to the west-that enabled the southward migration.)
Dome n穹顶
一些独具特色的建筑风格:
Mosque /mɑ:sk/n清真寺
Gothic /ˈgɑ:θɪk/ adj哥特式的(12至16世纪流行于西欧的建筑风格,以尖拱、尖窗和细长柱为特色)
Pyramid /ˈpɪrəmɪd/ n金字塔
(TPO39 passage1 which explains why it was carved on walls of pyramids and other religious structures.)
Baroque /bəˈroʊk/ n巴洛克(17至18世纪早期流行于欧洲,气势雄伟、装饰华丽的特色)
Skyscraper /ˈskaɪskreɪpə(r)/ n摩天大楼
(TPO23 passage1 On the other hand, air turbulence increases because of the effect of skyscrapers on airflow.)
建筑类文章,通常选取的建筑都是有一定历史年限的,而这些古代的建筑中,岩石材料是最容易获取并且使用最广泛的材料之一,文章中还会对不同的岩石进行简单的介绍,如果我们能够了解这些岩石的形成原因和名字,在阅读或听力中,也能够帮助我们快速快速get到描写对象,不至于一头雾水啦:

Igneous /ˈɪgniəs/ n火成岩(火山喷发后凝固的岩石)
Granite /ˈgrænɪt/ n花岗岩
Scoria /'skorɪr/ n铁矿,铁渣
Pumice /ˈpʌmɪs/ n浮岩,浮石
Obsidian /əbˈsɪdiən/ n黑曜岩,黑曜石
(TPO1 lecture3 And um... obsidian is a black, volcanic, well, almost like glass. It flakes very nicely into really sharp points.)
Sedimentary n沉积岩
(TPO39 lecture1 Stromatolites look like wavy layers ofsedimentary rock, but they are really fossils, fossils of the waste from microbial masts)
Sandstone n砂岩
Limestone /ˈlaɪmstoʊn/ n石灰岩
(TPO41 passage2 it is either dissolved in the oceans or chemically bound into carbonate rocks, such as the limestone and marble that formed in the oceans.)
Shale /ʃeɪl/ n页岩
Conglomerate /kənˈglɑ:mərət/ n砾岩
Gypsum /ˈdʒɪpsəm/ n石膏
Metamorphic /ˌmetəˈmɔ:rfɪk/ adj变质的
Marble /ˈmɑ:rbl/ n大理石
(TPO42 lecture1 I am sure you've all been to museum, where you've seen beautiful white marble statues sculpted by the Greeks and Romans)
Slate /sleɪt/ n板岩
Quartzite /'kwɔrts,aɪt/ n石英岩
Gneiss /naɪs/ n片麻岩
了解完建筑的种类的建筑材料,让我们进入内部来看看,房间中不同的分区及这些分区中都有些什么常见的设施:
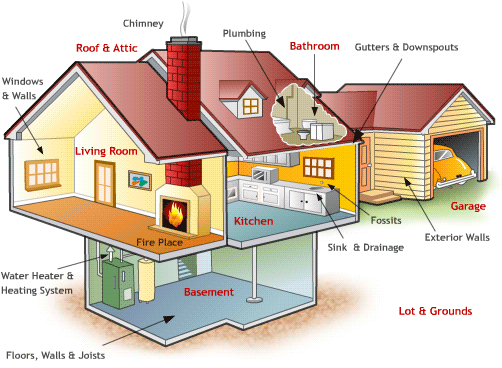
Roof& Attic 屋顶阁楼
Lot& Grounds 地段地面
Garage /gəˈrɑ:ʒ; gəˈrɑ:dʒ/ n车库
Gutter /ˈgʌtə(r)/ n檐沟
Downspout /ˈdaʊnspaʊt/ n水落管(用于排水)
Fireplace n壁炉
(TPO3 lecture4 when a fireplace leaves behind a lot of phosphorus in the soil, we'd also find an unusually high concentration of potassium.)
Chimney /ˈtʃɪmni/ n烟囱
(TPO11 lecture2 Now what can you tell me about the chimney, about its location?)
Heating system 取暖系统
Sink /sɪŋk/ n洗涤池,洗碗槽
Drainage /ˈdreɪnɪdʒ/ n排水系统
Plumbing /ˈplʌmɪŋ/ n管路系统,自来水管道
Joist /dʒɔɪst/ n隔栏,脱梁
Exterior wall 外墙
古代的建筑,因为建筑技术和建筑材料获取的局限性,只要求遮风避雨即可,远古时期的人类更是直接居住在山洞里面,但随着建筑技术的发展和人类不断提高的要求,对建筑的要求也越来越高,我们来看看怎么表达吧:
Prevent /prɪˈvent/ v妨碍,防止
fire-prevention 防火
earthquake /ˈɜ:rθkweɪk/ n地震
quake-proof 防震
anti-corrosion 防腐
dump-proof 防潮
water-proof 防水
dust-proof 防尘
rust-proof 防锈
最后是一些相关词汇小总结:
cohere /koʊˈhɪr/ v粘合
component / kəmˈpoʊnənt/ n零件
(TPO51 passage A fluid is a substance, such as a liquid or gas, in which the component particles can move past one another.)
layout n布局
parallel /ˈpærəlel/ adj平行的
vertical / ˈvɜ:rtɪkl/ adj垂直的
(TPO3 lecture1 where the weight is borne by the vertical elements on either side of the arch.)
symmetrical /sɪˈmetrɪkl/ adj对称的
更多雅思考试备考相关资讯请持续关注http://youth.gedu.org

 Recommend
Recommend 阅读:2028
阅读:2028
 阅读:539
阅读:539
 阅读:572
阅读:572
 阅读:422
阅读:422
 阅读:1132
阅读:1132
北京环球天下教育科技有限公司 版权所有 | 投诉热线:010-61043630 | 工作时间:9:00-18:00 | 投诉邮箱:tousu@pxjy.com
Copyright 1997-2025 gedu.org. All Right Reserved 京ICP备10036718号